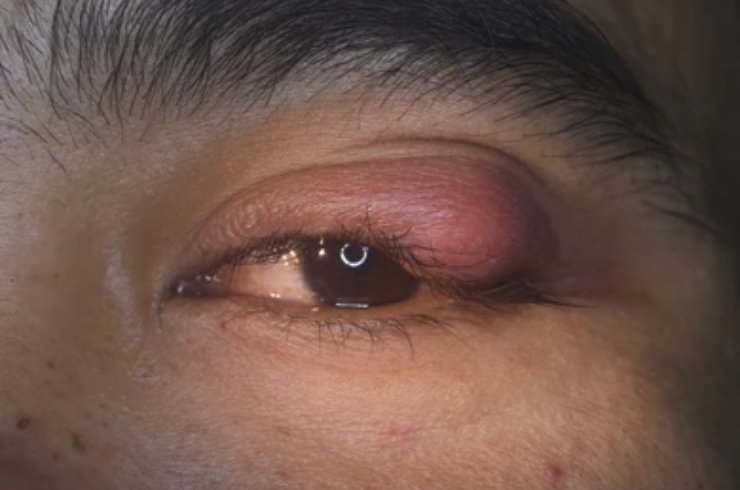
Orbital diseases involve the structures surrounding the eye, including muscles, fat, and bones, and may result from infections, tumors, trauma, or inflammatory conditions.
Comprehensive care for orbital diseases ensures functional recovery, improved appearance, and better quality of life.